A coculture of Enterobacter and Comamonas reduces Cd accumulation in rice
Arthor:Xing Wang, Qing Xu, Kang Hu, Gejiao Wang and Kaixiang Shi
Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions. Jan 24 2023
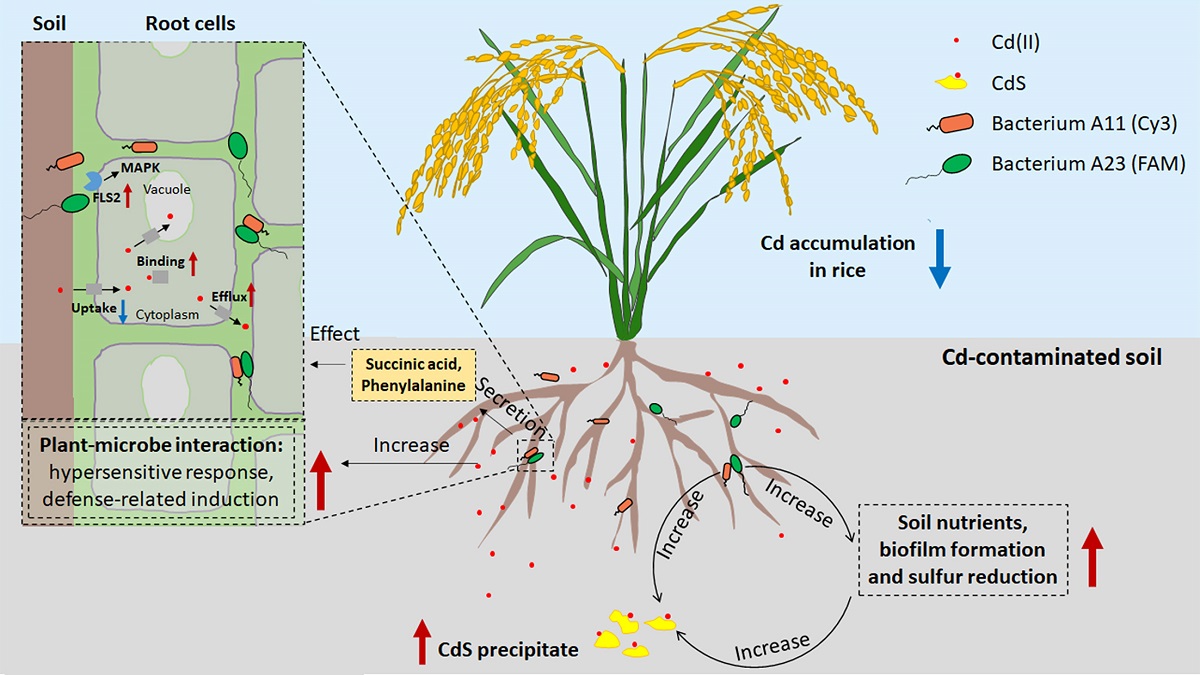
Abstract:The accumulation of cadmium (Cd) in plants is strongly impacted by soil microbes, but its mechanism remains poorly understood. Here, we report the mechanism of reduced Cd accumulation in rice by coculture of Enterobacter and Comamonas. In pot experiments, inoculation with the coculture decreased Cd content in rice grain and increased non-bioavailable Cd amount in Cd-spiked soils. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) detection showed that the coculture colonized in the rhizosphere and rice roots' vascular tissue and intercellular space. Soil metagenomics data showed that the coculture increased the abundance of sulfate reduction and biofilm formation genes and related bacterial species. Moreover, the coculture increased the content of organic matter, available nitrogen, and potassium, and increased the activities of arylsulfatase, β-galactosidase, phenoloxidase, arylamidase, urease, dehydrogenase, and peroxidase in soils. In subsequent rice transcriptomics assays, we found that the inoculation with coculture activated hypersensitive response, defense-related induction, and MAPK signaling pathway in rice. Heterologous protein expression in yeast confirmed the function of four Cd binding proteins (HIP28-1, HIP28-4, BCP2, and CID8), a Cd efflux protein (BCP1), and three Cd uptake proteins (COPT4, NRAM5, and HKT6) in rice. Succinic acid and phenylalanine were subsequently proved to inhibit rice Cd(II) uptake and activate Cd(II) efflux in rice roots. Thus, we propose a model that the coculture protects rice against Cd stress via Cd immobilization in soils and reducing Cd uptake in rice.
Full Article:https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-09-22-0186-R